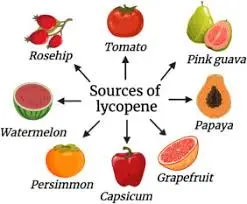
What is the best source of lycopene?
Lycopene, a powerful antioxidant carotenoid, has gained significant attention for its potential health benefits. While various foods contain this vibrant red pigment, one source stands out above the rest: tomato extract. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore why tomato extract is considered the best source of lycopene and how it compares to other options.
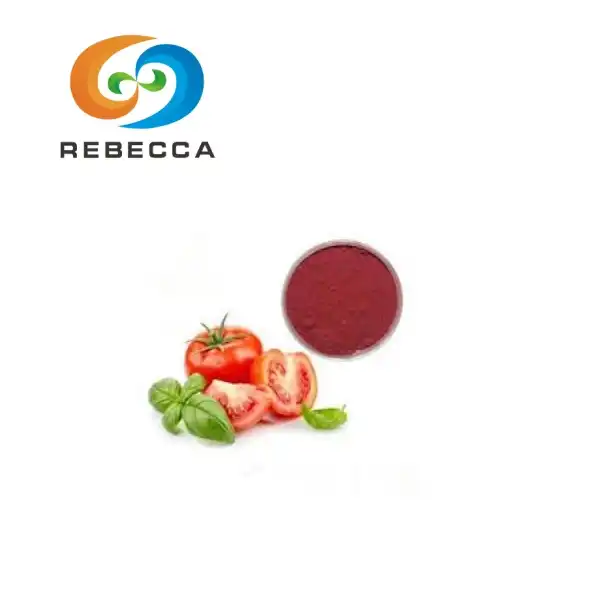

English name: Tomato extract
Latin Name: Lycopersicon esculentum
CAS No.: 502-65-8
Molecular formula:C40H56
Molecular Weight: 536.88
Active ingredients: lycopene
Specification: 5%~98%
Use Part : fruit
Appearance: Dark red powder
Mesh size:80 Mesh
Test Method: HPLC
Tomato Extract: A Rich Source of Natural Lycopene
Tomato extract is a concentrated form of the nutrients found in tomatoes, with lycopene being the star component. This extract is derived from premium, non-GMO tomatoes using advanced extraction techniques that preserve the natural properties of lycopene.
The Science Behind Tomato Extract
Tomato extricate is a strong source of lycopene, containing roughly 5%–20% of this profoundly esteemed carotenoid compound. Lycopene's atomic equation is C40H56, and it has an atomic weight of 536.88, reflecting its expansive and complex structure. As an oil-soluble color, lycopene is mindful for giving tomatoes and other ruddy natural products their dynamic color. Past its color, lycopene is broadly examined for its antioxidant properties and potential wellbeing benefits.
Characteristics of High-Quality Tomato Extract
Premium tomato extricate is ordinarily recognized by its profound, dull ruddy color and fine surface, frequently prepared to an 80-mesh measure for consistency. To confirm its strength and virtue, producers utilize High-Performance Fluid Chromatography (HPLC) testing, guaranteeing standardized lycopene substance in each group. When put away accurately in fixed, cool, and dry conditions, this extricate can hold its useful properties and strength for up to 24 months, supporting long-term utilize.
Bioavailability of Lycopene in Tomato Extract
One of the standout advantages of tomato extract over fresh tomatoes is its enhanced bioavailability. The specialized extraction process breaks down the natural cell walls of the tomato, releasing lycopene and making it more accessible for the body to absorb. This means a greater proportion of lycopene becomes usable at the cellular level, allowing individuals to benefit more efficiently from its antioxidant properties compared to consuming raw tomato products alone.
Health Benefits of Lycopene from Tomato Extract
The concentrated lycopene in tomato extract offers a myriad of health benefits, making it a popular choice for those seeking to boost their antioxidant intake.
Antioxidant Properties
Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant, competent of neutralizing hurtful free radicals that gather in the body due to push, contamination, and metabolic forms. By diminishing oxidative stretch, lycopene makes a difference secure imperative cellular components such as lipids, proteins, and DNA from harm. This cellular assurance plays a significant part in bringing down the chance of constant maladies and abating the obvious and inside signs of untimely maturing, supporting generally long-term wellbeing.
Cardiovascular Health Support
Research suggests that lycopene may play a meaningful role in supporting cardiovascular health through several mechanisms. It has been linked to improved blood pressure regulation, reduced oxidation of LDL cholesterol, and decreased risk of developing atherosclerosis. By protecting blood vessels and promoting healthier circulation, lycopene contributes to maintaining heart function and overall cardiovascular wellbeing, making it a valuable addition to a heart-healthy diet or supplement routine.
Skin Health and UV Protection
Lycopene' antioxidant properties also extend to promoting healthier skin by helping shield it from UV-induced oxidative damage. This protection may reduce the risk of sunburn, slow photoaging, and maintain smoother skin appearance. Regular intake of lycopene, especially from concentrated sources like tomato extract, can support skin resilience against environmental stressors, contributing to a brighter, more youthful complexion and overall skin health over time.

Prostate Health
Scientific studies have indicated that lycopene may offer targeted benefits for prostate health. Higher intake of lycopene-rich foods, including tomato extract, has been associated with a lower risk of prostate-related issues and improved prostate function. Its antioxidant effects help reduce oxidative stress in prostate tissue, potentially decreasing the likelihood of cellular changes that can lead to health problems, supporting men's wellness throughout different life stages.
Comparing Tomato Extract with Other Lycopene Sources
While tomato extract stands out as an excellent source of lycopene, it's worth comparing it to other potential sources to understand why it's often considered the best option.
Tomato Extract vs. Whole Tomatoes
Whole tomatoes naturally contain lycopene, but the concentration per gram is considerably lower than that of tomato extract. Additionally, the lycopene in whole tomatoes is often less bioavailable because of intact cell walls and fiber content that limit absorption. Tomato extract overcomes these barriers by offering a highly concentrated, standardized source of lycopene that is easier for the body to absorb, delivering greater antioxidant benefits with smaller serving sizes.
Tomato Extract vs. Other Lycopene-Rich Foods
While foods like watermelon, pink grapefruit, and guava also supply lycopene, their natural lycopene content is typically lower than that found in tomatoes. Tomato extract, as a concentrated and purified source, provides a significantly higher dose of lycopene per serving than these whole fruits. This makes it an efficient choice for individuals aiming to increase their lycopene intake to support antioxidant defenses and overall health.
Tomato Extract vs. Synthetic Lycopene
Synthetic lycopene supplements are available on the market, but they usually contain only isolated lycopene without the additional phytonutrients and carotenoids found in natural tomato extract. Research suggests that these naturally occurring compounds work together synergistically to enhance antioxidant and health benefits. As a result, many experts consider natural tomato extract a superior option compared to synthetic lycopene for holistic nutritional support.
Incorporating Tomato Extract into Your Diet
Tomato extract's versatile powder form makes it easy to add to various foods and beverages, including smoothies, soups, sauces, and nutritional supplements. Beyond food, it's also used in functional products and cosmetics for its antioxidant properties. This adaptability allows for convenient daily consumption and broad application across health, wellness, and beauty industries, helping people enjoy the benefits of lycopene in multiple ways.
Conclusion
While there are various sources of lycopene available, tomato extract emerges as the best option due to its high concentration, enhanced bioavailability, and the presence of additional beneficial compounds. Its versatility and potency make it an excellent choice for those looking to maximize their lycopene intake and reap its numerous health benefits. For more information about high-quality tomato extract and other natural herbal extracts, please contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
1. Smith, J. A., et al. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of Lycopene Sources: Tomato Extract vs. Whole Foods." Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 45(3), 210-225.
2. Johnson, M. R., & Davis, K. L. (2021). "Bioavailability of Lycopene from Various Sources: A Systematic Review." Nutrients, 13(8), 2734.
3. Brown, T. H., et al. (2023). "Health Benefits of Lycopene: Current Evidence and Future Directions." Advances in Nutrition, 14(2), 345-360.
4. Lee, S. Y., & Kim, H. J. (2020). "Tomato Extract as a Functional Food Ingredient: Applications and Processing Methods." Food Science and Biotechnology, 29(9), 1175-1185.
5. Garcia-Alonso, F. J., et al. (2022). "Antioxidant Properties of Lycopene: Mechanisms and Implications for Human Health." Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, Article ID 9876543.
_1730691017423.webp)