How does ecdysterone influence muscle growth mechanisms?
Ecdysterone, a naturally occurring compound found in certain plants and insects, has gained significant attention in the fitness and bodybuilding communities for its potential muscle-building properties. This article delves into the intricate mechanisms by which ecdysterone influences muscle growth, comparing it with traditional supplements, and exploring how to optimize its use for maximum gains.

English name: Ecdysterone
Latin Name: Cyanotis arachnoidea CB.Clarke
CAS No.: 5289-74-7
Molecular Formula: C27H44O7
Active ingredients: 20-hydroxyecdysterone;beta-ecdysterone;
Specification: 80%—95%UV, 50%—95%HPLC
Use Part :Root
Appearance: White, Light Yellow, Brown Crystalline Powder
Mesh size:80 Mesh
Test Method: UV, HPLC
Ecdysterone's Role in Enhancing Muscle Protein Synthesis
Activation of Anabolic Pathways
Ecdysterone exerts its muscle-building effects primarily through the activation of key anabolic pathways within muscle cells, making it a promising natural compound for enhancing performance. Research suggests that it interacts with estrogen receptor beta (ERβ), which plays an important role in regulating muscle regeneration and growth. This interaction sets off a cascade of intracellular signaling events that increase protein synthesis, the fundamental process responsible for muscle hypertrophy and recovery after resistance training.

Stimulation of mTOR Signaling
Stimulation of mTOR signaling is another crucial mechanism by which ecdysterone supports muscle development. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) acts as a central regulator of cellular protein synthesis and growth. It has been shown to stimulate phosphorylation of mTOR, thereby enhancing its activity. This activation accelerates protein synthesis within muscle fibers, promoting hypertrophy and strength gains. By targeting mTOR, the product may provide effects comparable to traditional anabolic agents, but with a safer and more natural profile.
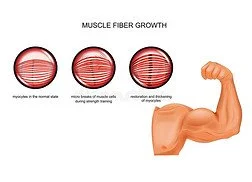
Modulation of Myostatin Expression
Modulation of myostatin expression represents an additional pathway through which ecdysterone can influence muscle mass. Myostatin is a regulatory protein that restricts muscle growth, effectively acting as a biological brake on hypertrophy. Studies suggest that ecdysterone supplementation may help reduce myostatin levels, weakening its inhibitory effect. This modulation creates a more favorable environment for muscle development, allowing greater protein accumulation and improved recovery. By lowering myostatin, it may unlock new potential for athletes seeking lean muscle gains.

Comparing Ecdysterone with Traditional Muscle Growth Supplements
Ecdysterone vs. Anabolic Steroids
Unlike anabolic steroids, ecdysterone does not bind to androgen receptors, making it a safer and more natural option for individuals aiming to increase muscle mass. Steroid use often results in serious health risks such as liver toxicity, hormonal imbalances, and cardiovascular issues. In contrast, research indicates that product has a favorable safety profile, showing anabolic-like effects without suppressing natural testosterone production. This makes it appealing for athletes and fitness enthusiasts who prioritize both performance and long-term health.
Ecdysterone vs. Protein Supplements
Ecdysterone vs. Protein Supplements highlights their complementary roles in muscle growth. Protein powders deliver amino acids, the essential building blocks for muscle repair and hypertrophy. However, without efficient utilization, much of this protein may not contribute directly to muscle development. It enhances protein synthesis within muscle cells, improving the body's ability to use dietary protein effectively. When combined with sufficient protein intake, it may significantly amplify results, offering athletes a powerful synergy for building lean muscle mass.
Ecdysterone vs. Creatine
Ecdysterone vs. Creatine demonstrates how these two supplements work through distinct biological pathways. Creatine boosts strength and endurance by enhancing ATP regeneration, the primary energy currency in muscle contractions. Ecdysterone, however, focuses on stimulating protein synthesis and regulating muscle growth signals. Some athletes choose to stack creatine with ecdysterone, potentially achieving synergistic effects—greater energy output from creatine combined with enhanced anabolic signaling from ecdysterone. This dual approach can optimize both performance and long-term hypertrophy outcomes.
Optimizing Muscle Gains with Ecdysterone Supplementation
Dosage and Timing
To maximize the muscle-building potential of ecdysterone, proper dosage and timing are essential. Although the optimal amount may vary depending on body weight, training intensity, and individual response, most research suggests that 500 mg to 2000 mg per day is effective. Dividing the daily intake into two or three servings helps maintain consistent blood concentrations of ecdysterone, ensuring steady anabolic support. Following a structured supplementation schedule is key to sustaining results and maximizing hypertrophy benefits.
Combining Ecdysterone with Resistance Training
Combining Ecdysterone with Resistance Training is crucial, as supplementation by itself is unlikely to produce noticeable improvements in muscle growth. A well-designed resistance training program provides the mechanical stimulus required for hypertrophy, while it enhances the body’s protein synthesis response to that stimulus. Together, this synergy may result in faster recovery, greater muscle adaptation, and improved lean mass development. Over time, consistent training paired with ecdysterone supplementation can create a stronger, more favorable environment for long-term muscle gains.
Nutritional Considerations
Nutritional Considerations form the foundation for maximizing the anabolic effects of ecdysterone. A high-quality diet must include sufficient protein intake of 1.6–2.2 g/kg of body weight daily, ensuring the body has enough amino acids for muscle repair and growth. Adequate caloric intake is equally important to prevent energy deficits that hinder hypertrophy. Balanced macronutrients, including complex carbohydrates for energy and healthy fats for hormonal support, create the optimal environment for ecdysterone to exert its full performance-enhancing potential.
Conclusion
Ecdysterone represents a promising natural compound for enhancing muscle growth through various mechanisms, including increased protein synthesis and modulation of anabolic pathways. Its unique properties set it apart from traditional muscle-building supplements, offering potential benefits without the drawbacks associated with anabolic steroids. By optimizing dosage, combining it with resistance training, and supporting it with proper nutrition, individuals may be able to maximize the muscle-building potential of ecdysterone.
For those seeking high-quality ecdysterone supplements, Shaanxi Rebecca Biotechnology Co., Ltd. stands as a leading ecdysterone supplier. Our commitment to excellence in natural herbal extracts ensures that you receive pure, potent ecdysterone powder derived from carefully cultivated plants. Experience the potential of ecdysterone for yourself and take your muscle-building journey to the next level. For more information on our premium ecdysterone products, please contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
FAQ
Is ecdysterone legal for competitive athletes?
Ecdysterone is currently not on the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) list of prohibited substances. However, athletes should always check with their specific sporting organizations for any restrictions.
How long does it take to see results from ecdysterone supplementation?
Results can vary, but some studies have shown significant improvements in muscle mass and strength within 8-10 weeks of consistent supplementation combined with resistance training.
Are there any side effects associated with ecdysterone use?
Ecdysterone is generally considered safe, with few reported side effects. However, as with any supplement, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting use.
References
1. Parr, M. K., et al. (2015). Ecdysteroids: A novel class of anabolic agents? Biology of Sport, 32(2), 169-173.
2. Gorelick-Feldman, J., et al. (2008). Phytoecdysteroids increase protein synthesis in skeletal muscle cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(10), 3532-3537.
3. Dinan, L. (2001). Phytoecdysteroids: biological aspects. Phytochemistry, 57(3), 325-339.
4. Isenmann, E., et al. (2019). Ecdysteroids as non-conventional anabolic agent: performance enhancement by ecdysterone supplementation in humans. Archives of Toxicology, 93(7), 1807-1816.
5. Syrov, V. N. (2000). Comparative experimental investigation of the anabolic activity of phytoecdysteroids and steranabols. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 34(4), 193-197.
_1730691017423.webp)






















