Creatine Monohydrate vs Creatine HCL: Which Is Better?
In the world of fitness supplements, creatine stands out as a powerhouse for enhancing athletic performance and muscle growth. Two popular forms of this supplement have been dominating the market: creatine monohydrate and creatine hydrochloride (HCL). This article delves into the differences between these two forms, focusing on the benefits of the best pure creatine monohydrate and helping you make an informed decision for your fitness journey.
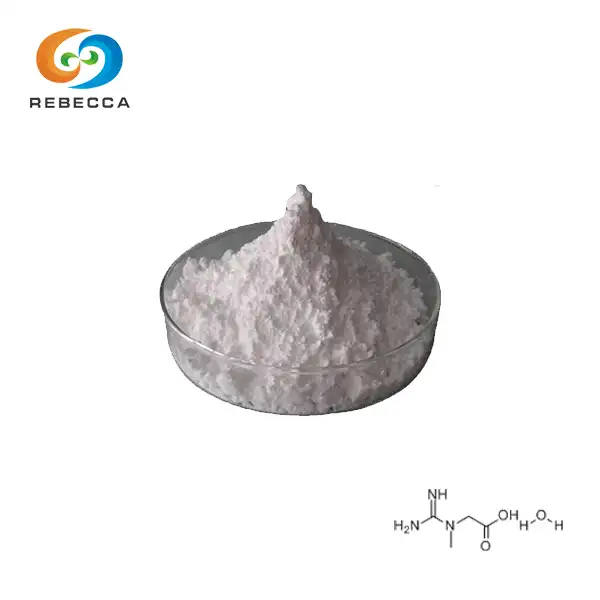

【Product name】: Creatine Monohydrate
【Specification】 99.5%-102.0% 【CAS No.】: 6020-87-7
【Molecular Formula】: C4H11N3O3
【Appearance】:White crystal or white powder
【Test Method】: HPLC
Benefits of the Best Pure Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate has been the gold standard in creatine supplementation for decades, and for good reason. The best pure creatine monohydrate offers a myriad of benefits that have been extensively researched and proven effective:
Enhanced Athletic Performance
One of the primary benefits of best pure creatine monohydrate is its ability to significantly improve athletic performance. By increasing the body's phosphocreatine stores, it provides a rapid energy source for high-intensity, short-duration activities. This translates to improved power output, allowing athletes to push harder and longer during workouts or competitions.

Increased Muscle Mass
Creatine monohydrate has been shown to promote muscle growth by enhancing protein synthesis and reducing protein breakdown. This anabolic effect leads to greater muscle mass gains when combined with resistance training. The best pure creatine monohydrate can help athletes and bodybuilders achieve their muscle-building goals more effectively.

Improved Recovery
Another significant advantage of the best pure creatine monohydrate is its ability to accelerate post-workout recovery. By reducing muscle damage and inflammation, it helps athletes bounce back faster between training sessions. This improved recovery can lead to more consistent and productive workouts over time.
Cognitive Benefits
While often overlooked, creatine monohydrate also offers cognitive benefits. Research suggests that it may improve memory and cognitive function, particularly in situations of sleep deprivation or mental fatigue. This makes it a valuable supplement not just for athletes, but for anyone looking to enhance their mental performance.

Cost-Effective
Compared to other forms of creatine, including creatine HCL, best pure creatine monohydrate is typically more affordable. Its well-established manufacturing process and widespread availability make it a cost-effective option for those looking to incorporate creatine into their supplement regimen.
How to Choose the Best Pure Creatine Monohydrate?
Selecting the right creatine monohydrate supplement is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing the best pure creatine monohydrate:
Purity and Quality
Look for products that offer high purity levels, ideally 99% or higher. The best pure creatine monohydrate should be free from contaminants and unnecessary additives. Check for third-party testing certifications to ensure the product meets quality standards.
Micronization
Micronized creatine monohydrate has been processed to create smaller particles, which can improve solubility and absorption. This can lead to better mixability in liquids and potentially enhanced effectiveness.
Brand Reputation
Choose reputable brands with a history of producing high-quality supplements. Look for companies that are transparent about their sourcing and manufacturing processes, such as Shaanxi Rebecca Bio-Tech Co., LTD, known for their commitment to quality and purity in natural products.
Form and Packaging
Creatine monohydrate is available in various forms, including powder, capsules, and tablets. Powder is often the most versatile and cost-effective option. Consider packaging that protects the product from moisture, as creatine can degrade when exposed to water.
Dosage and Serving Size
Check the recommended dosage and serving size to ensure it aligns with your supplementation goals. The standard dose for creatine monohydrate is typically 5 grams per day, but this can vary based on individual needs and body weight.

Creatine Monohydrate vs HCL: Key Differences Explained
While both creatine monohydrate and creatine HCL aim to provide similar benefits, there are notable differences between the two forms:
Solubility and Absorption
Creatine HCL is often marketed as having superior solubility compared to creatine monohydrate. While it does dissolve more easily in water, this doesn't necessarily translate to better absorption or effectiveness. The best pure creatine monohydrate, especially when micronized, has excellent bioavailability and has been proven effective through numerous studies.
Dosage Requirements
Proponents of creatine HCL claim that it requires a lower dose to achieve the same effects as creatine monohydrate. However, scientific evidence supporting this claim is limited. The well-established dosage protocol for creatine monohydrate (5 grams per day) has been extensively researched and proven effective.
Research Backing
Creatine monohydrate has decades of research supporting its safety and efficacy. It's been studied in various populations, including athletes, older adults, and individuals with certain medical conditions. In contrast, creatine HCL has limited research specifically comparing its effectiveness to creatine monohydrate.
Cost and Availability
Best pure creatine monohydrate is generally more affordable and widely available compared to creatine HCL. Its established manufacturing process and popularity contribute to its lower cost, making it a more accessible option for many consumers.
Potential Side Effects
Both forms of creatine are generally considered safe when used as directed. However, some users report fewer gastrointestinal issues with creatine HCL compared to monohydrate. It's worth noting that these effects are typically mild and can often be mitigated by proper hydration and dosing strategies with creatine monohydrate.
Conclusion
While both creatine monohydrate and creatine HCL have their merits, the best pure creatine monohydrate remains the most well-researched and reliable form of creatine supplementation. Its proven track record in enhancing athletic performance, increasing muscle mass, and improving recovery makes it a top choice for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike. When choosing a creatine supplement, factors such as purity, quality, and brand reputation should be prioritized to ensure optimal results.
At Shaanxi Rebecca Bio-Tech Co., LTD, we pride ourselves on offering the highest quality best pure creatine monohydrate. Our advanced production processes, including high-temperature drying and ultra-fine grinding, ensure maximum purity and bioavailability. Experience the difference that premium creatine monohydrate can make in your fitness journey. For more information about our natural herbal extracts and supplements, please contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
FAQs
Is best pure creatine monohydrate safe for long-term use?
Yes, numerous studies have shown that creatine monohydrate is safe for long-term use when taken as directed.
Can vegetarians and vegans use creatine monohydrate?
Absolutely. Our best pure creatine monohydrate is 100% vegan-friendly and suitable for all dietary preferences.
How long does it take to see results from creatine monohydrate supplementation?
Most users begin to notice benefits within 1-2 weeks of consistent use, with full effects typically seen after 4-8 weeks.
Do I need to cycle creatine monohydrate?
Cycling is not necessary for most users. Continuous use of creatine monohydrate is safe and effective for maintaining its benefits.
Can women take creatine monohydrate?
Yes, creatine monohydrate is equally beneficial and safe for both men and women looking to enhance their athletic performance and muscle growth.
References
1. Kreider, R. B., et al. (2017). International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine.
2. Cooper, R., et al. (2012). Creatine supplementation with specific view to exercise/sports performance: an update.
3. Gualano, B., et al. (2012). Exploring the therapeutic role of creatine supplementation.
4. Jäger, R., et al. (2011). Analysis of the efficacy, safety, and regulatory status of novel forms of creatine.
5. Buford, T. W., et al. (2007). International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: creatine supplementation and exercise.
_1730691017423.webp)





















